Virtual Machine Managers
Table of Contents
There are several VM managers and in this post I will show you the most popular ones.
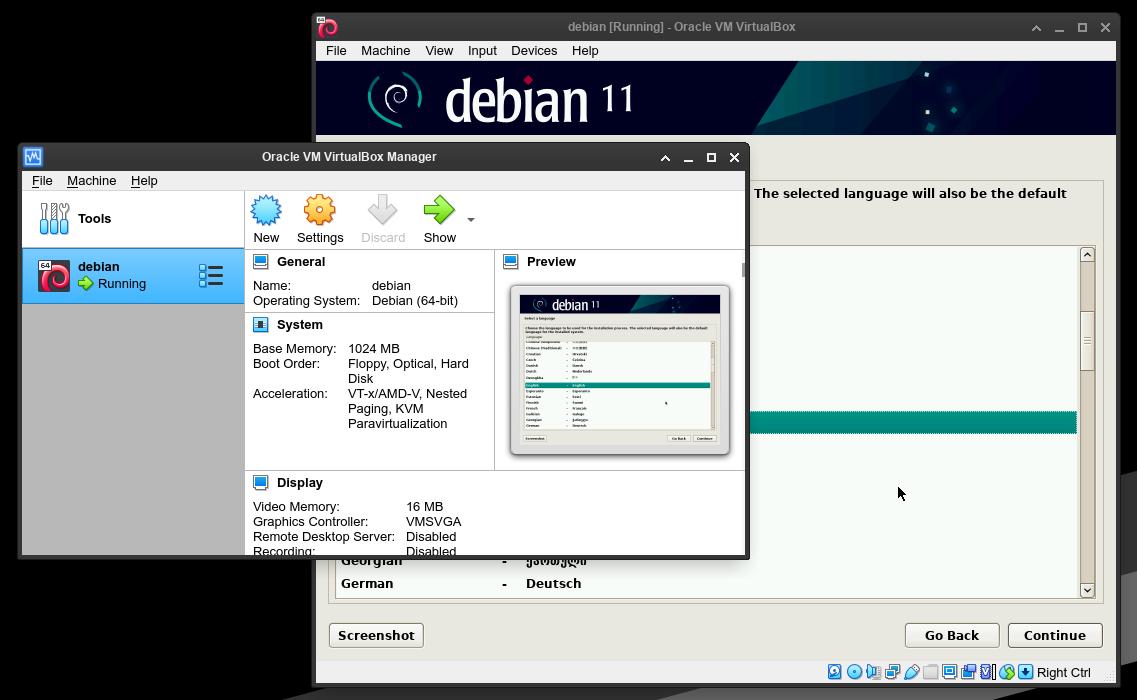
Oracle VirtualBox
One of the most popular VM managers on Linux and Windows. Easy to use.
QEMU
A command-line VM manager. You need a bit of learning to be able to use it but there are two main commands:
- Create a disk image:
qemu-img create disk.img <size>Replace <size> with the desired image size, e.g.: 256M.
More parameters:
-
-f <raw|qcow2>: specify image type. By default, it’sraw. -
Start a VM:
qemu-system-x86_64 disk.img- Add
-cdrom <iso file>or-fda <img file>to boot from an ISO image or an IMG floppy disk image. You can also start a VM with a physical disk inserted on a CD-ROM drive (-cdrom /dev/cdrom) or a physical USB stick (e.g.:-hda /dev/sdb, runlsblkto list block devices). - Another way of specifying a boot image is:
-drive file=<filename>. By Usingdriveparameter, you can specify more drive options (separated with commas), like the image format (format=<raw|qcow2>), the media type (media=<disk|cdrom>) or the interface (if=<ide|floppy|scsi|more...>).
qemu-system-x86_64 -drive file=windows101.img,format=raw,if=floppy-nographic: text-only output. Inside this mode, type Ctrl + A + H to exit QEMU.-nographic -vnc :0: derive output to a VNC server.-vnc :0 -daemonize: derive output to a VNC server and run in background.-m <number>: specify RAM size (you can add sufixes, likeMandG). This is probably the most important VM parameter because, by default, QEMU only assigns a minimum amount of RAM (128MB).-smp <number>: specify number of CPU cores to use.-enable-kvm: enable KVM full virtualization support. Improves perfomance.-monitor stdio: allows to manage QEMU from the terminal. You’ll see a command prompt that starts with(qemu). Inside this monitor, you can do a lot of things, like:- Mount a floppy image or change an already mounted one:
change floppy0 disk.img. - Eject a floppy:
eject floppy0. - Reset the VM:
system_reset. - Powerdown:
system_powerdown. - Close QEMU:
quit.
- Mount a floppy image or change an already mounted one:
virt-manager
A GUI frontend for QEMU.
GNOME Boxes
Download and run a Linux distro using the same program. More info on my post.
Quickemu
Similar to Boxes, but using the command-line. There is a GUI frontend (Quickgui), more info on this GUI and Quickemu on this post.
86box
A virtual machine manager focused on running old systems and software. Check [my post about 86box]({% post_url 2022-02-19-86box-emulator %}).
Multipass
Ubuntu VMs from Canonical. This virtual machine manager allows you to create Ubuntu VMs with just one command:
multipass launch ubuntuOnce VM is initialized, copy its name (look for the previous command output) and type:
multipass shell <vm name>
# multipass shell changeable-turkeyYou can also send commands to the VM:
multipass exec <vm name> -- <command>List launched VMs:
multipass listFind available images:
multipass findStop and delete a VM:
multipass stop <vm name>multipass delete <vm name>If you have any suggestion, feel free to contact me via social media or email.
Latest tutorials and articles:
Featured content: